Microsoft Sentinel All-in-One is aimed at helping customers and partners quickly set up a full-fledged Microsoft Sentinel environment that is ready to use by customers speeding up deployment and initial configuration tasks in few clicks, saving time and simplifying Microsoft Sentinel setup.
What’s new
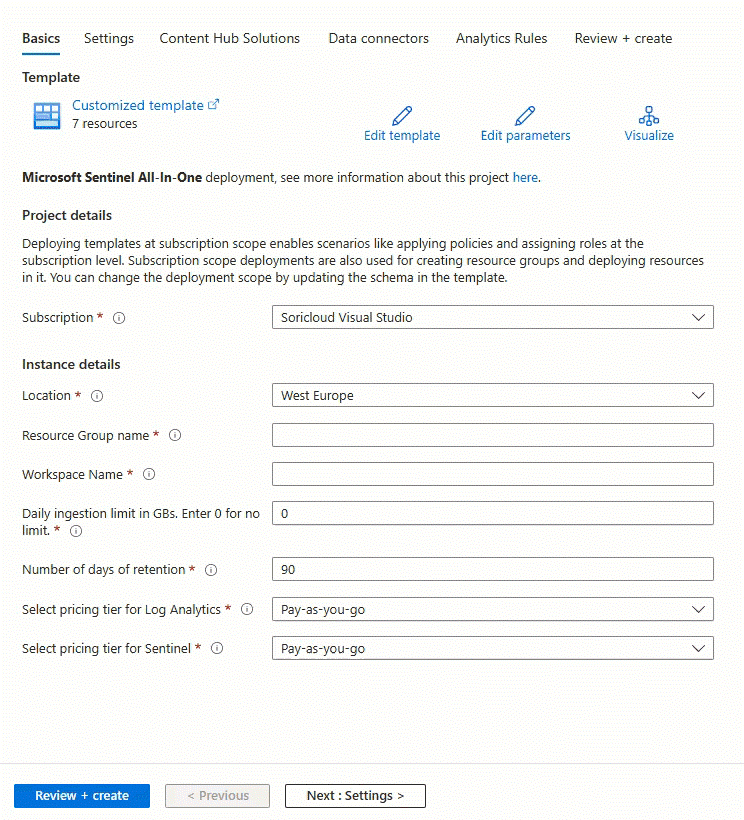
This new version automates the following steps:
- Creates resource group
- Creates Log Analytics workspace
- Enables Microsoft Sentinel on top of the workspace
- Sets workspace retention, daily cap and commitment tiers if desired
- Enables UEBA with the relevant identity providers (AAD and/or AD)
- Enables health diagnostics for Analytics Rules, Data Connectors and Automation Rules
- Installs Content Hub solutions from a predefined list
- Enables Data Connectors from this list:
- Azure Active Directory
- Azure Active Directory Identity Protection
- Azure Activity
- Dynamics 365
- Microsoft 365 Defender
- Microsoft Defender for Cloud
- Microsoft Insider Risk Management
- Microsoft Power BI
- Microsoft Project
- Office 365
- Threat Intelligence Platforms
- Enables analytics rules (Scheduled and NRT) included in the selected Content Hub solutions
- Enables analytics rules (Scheduled and NRT) that use any of the selected Data connectors
You can see a brief demo here:
Getting started
You can find this new version at http://aka.ms/sentinel-all-in-one.
The only thing you need to start using Microsoft Sentinel All-in-One, is an Azure Subscription and an account with permissions to deploy Microsoft Sentinel. Higher privileges might be required if you wish to enable UEBA and some of the supported connectors. You can find details about the required permissions here .
Source Microsoft.com