Image Source: Semperis
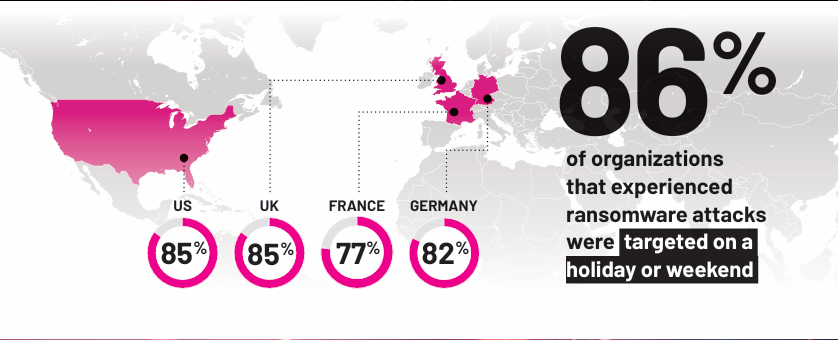
Ransomware attacks pose a significant threat year-round; however, they increase significantly during the busy holiday season. Cybercriminals often prepare to launch disruptive cyberattacks targeting multiple sectors, hiding in networks and waiting for the perfect moment to inflict maximum damage and compromise data without detection. A recent study revealed that 86 percent of surveyed organizations that fell victim to ransomware attacks across the United States, United Kingdom, France, and Germany were specifically targeted during holidays or weekends.
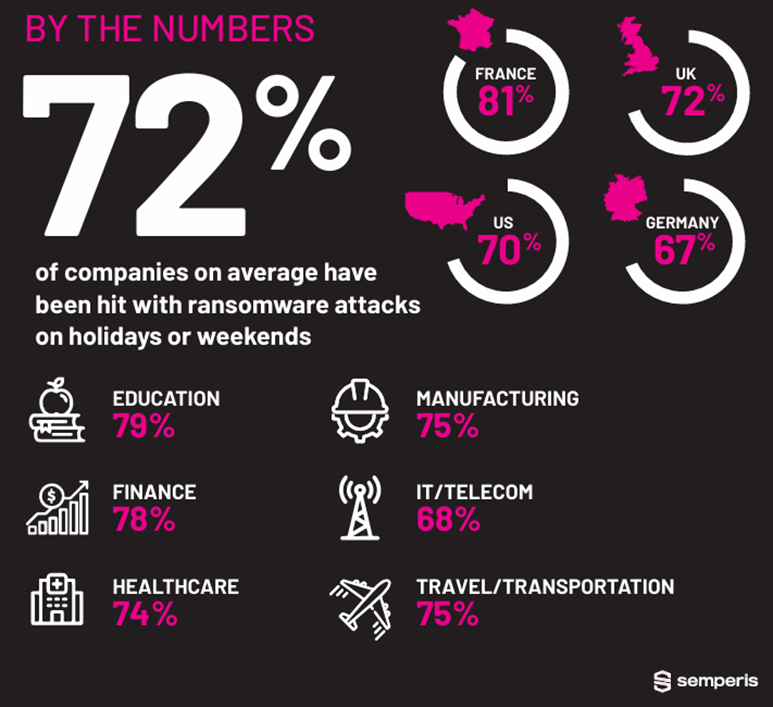
Additionally, threat actors consistently target critical infrastructure using advanced tactics to exploit critical operational IT systems. Campaigns notably prioritized industries and organizations with limited downtime, such as healthcare, financial services, and industrial operations. By focusing on environments where operational disruption can lead to cascading impacts, threat actors increase the likelihood of ransom payout, leveraging the criticality of uninterrupted services to pressure victims.
For example, a ransomware incident recently impacted Rhode Island’s RIBridges, a government system that manages many of the state’s social services programs. Hundreds of thousands of residents’ personal information—such as names, addresses, dates of birth, Social Security numbers, and banking details—was likely compromised.
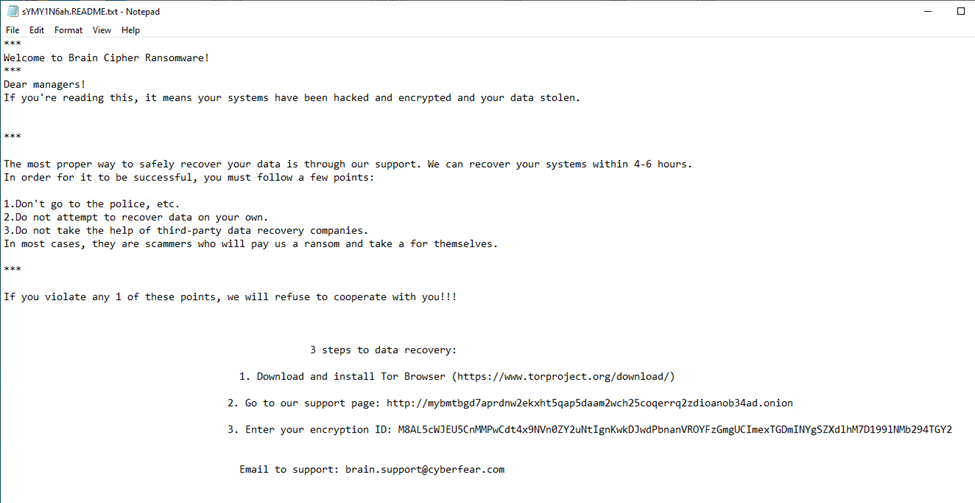
Brain Cipher ransom note. Image Source: WatchGuard
The ransomware group Brain Cipher is believed to have launched the attack on or before December 5. Brain Cipher is a ransomware operation that utilizes the leaked LockBit 3.0 (Black) builder for its encryptor. The group first became known after extorting the Indonesian government in mid-June 2024 and demanded an $8 million ransom.
Recent reports highlighted significant deficiencies in the state’s cybersecurity measures that required urgent attention, including insufficient resources to manage operations’ complexity and slow progress in risk mitigation. It also stressed the need to improve response capabilities for data breaches and mentioned a lack of specific insurance coverage for cybersecurity risks.
Furthermore, on November 21, the supply chain management firm Blue Yonder reported significant disruptions to its services due to a ransomware attack, specifically impacting grocery store chains in the UK. The managed services environment includes the Software as a Service (SaaS) platforms and cloud-hosted solutions for supply chain operations. Blue Yonder, a subsidiary of Panasonic and an Arizona-based cloud services provider that serves grocery stores, Fortune 500 firms, and a range of multinational corporations, generates over $1 billion in annual revenue. The company provides AI-driven supply chain solutions to prominent clients, including DHL, Starbucks, Walgreens, Kroger, Ford, and Tesco. This attack was likely calculated to coincide with the Thanksgiving holiday and disruptions in the supply chain could have left many grocery stores with empty shelves.
The Termite ransomware group claimed responsibility for this attack. They assert that they have stolen 680GB of data, which includes over 16,000 email lists intended for future attacks and more than 200,000 insurance documents. The group has claimed 10 victims worldwide, primarily focusing on Europe and North America. Targeted sectors include government agencies, education, disability support services, oil and gas, water treatment, and automotive manufacturing.
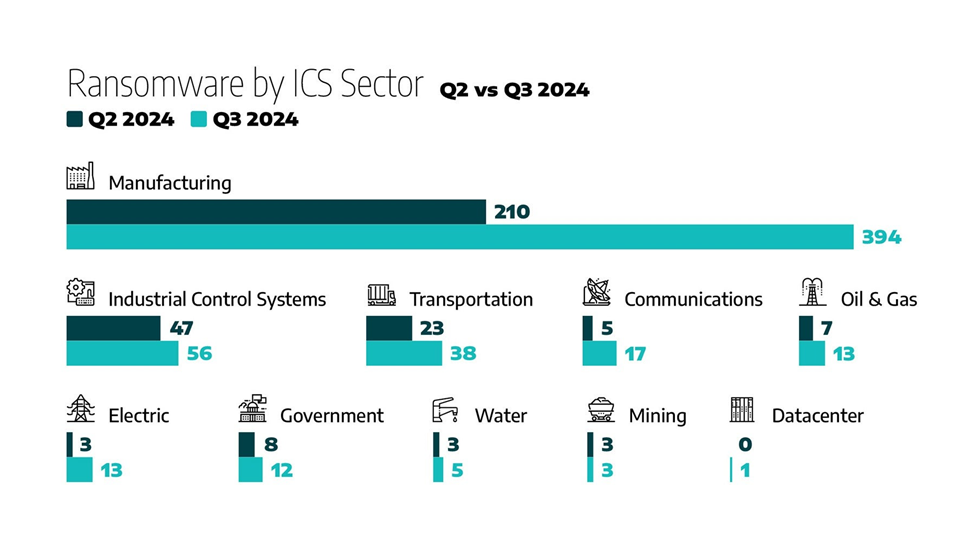
Ransomware Incidents by Sector: Q2 vs. Q3 2024. Image Source: Dragos
According to Dragos’ 2024 Third Quarter (Q3) Industrial Ransomware Analysis report, analysts observed the emergence of several new and established ransomware groups impacting industrial organizations. Several recent vulnerabilities were identified as initial access vectors used by threat actors targeting government and critical infrastructure sectors. Additionally, vulnerable remote and virtual private network (VPN) applications were exploited for initial access and post-compromise.
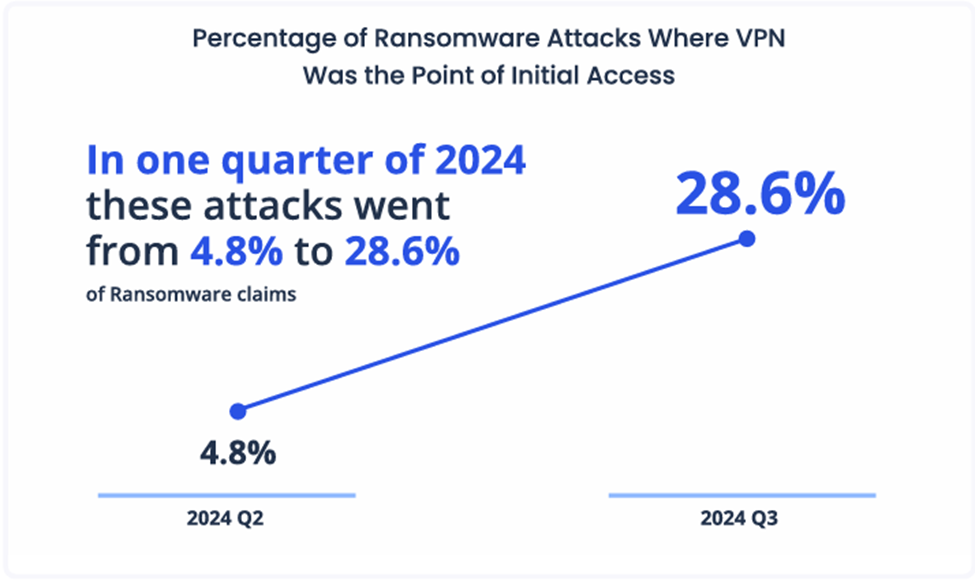
Image Source: Corvus Insurance
Approximately 30 percent of ransomware incidents during the third quarter were linked to vulnerabilities in VPN appliances, such as CVE-2024-40766, which impacts SonicWall SSL VPNs, or poorly managed credentials. Ransomware groups have also combined vulnerability exploitation with credential-based attacks to bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA) protections. They employ credential stuffing, pass-the-hash attacks, and brute force techniques. Compromised credentials, often sourced from Initial Access Brokers (IABs), have become central to their tactics. In 2023, cybercriminals extorted a record $1.1 billion in ransom payments from organizations worldwide despite the US government’s efforts to disrupt their financial operations.
New Jersey law requires state and local government agencies, public education institutions, and government contractors to report any cyber incidents within 72 hours. This legislation applies to a wide range of entities, including public K-12 schools, public higher education institutions, state law enforcement agencies, counties, municipalities, and more.
Recommendations
- Refrain from clicking links, responding to, or acting on unsolicited emails.
- Navigate directly to legitimate websites and verify before submitting account credentials or providing personal or financial information.
- Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts and enable MFA where available, choosing authentication apps or hardware tokens over SMS text-based codes.
- Keep systems up to date and apply patches after appropriate testing.
- Maintain robust and up-to-date endpoint detection tools on every endpoint.
- Consider leveraging behavior-based detection tools rather than signature-based tools.
- Utilize network segmentation to isolate valuable assets and help prevent the spread of ransomware and malware.