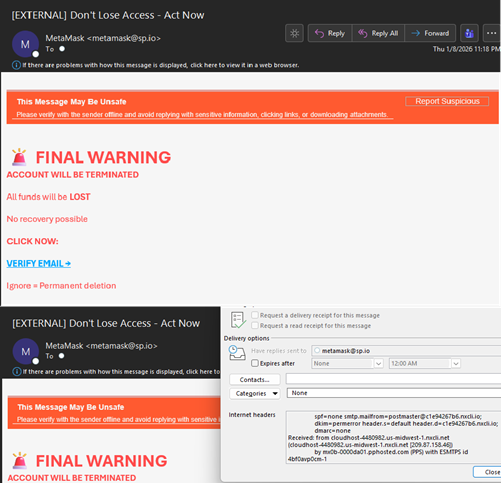
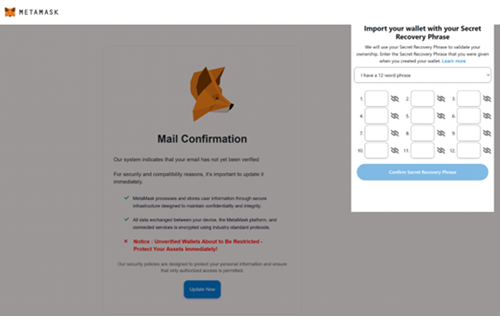
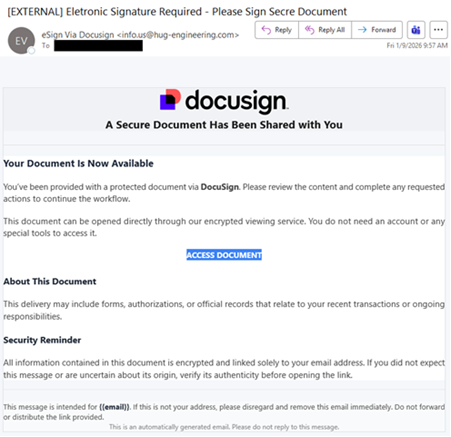
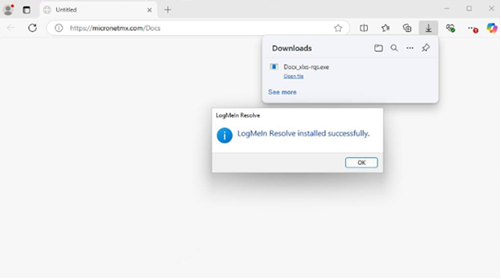
| If the link is clicked, the target is directed to a malicious website, hxxps://micronetmx[.]com/Docs, that automatically downloads an executable called “Docx_xlxs-rqs[.]exe.” Clicking on the “Open file” link installs the LogMeIn Resolve RMM tool, allowing threat actors to remotely control the compromised device. Further analysis reveals that the executable file performs various tasks, including establishing persistence, checking the BIOS and system information in the registry, reviewing the system for installed applications, and dropping files into the System32 directory. The malicious use of RMM tools and weak organizational IT policies can lead to unauthorized access, persistent backdoor access, lateral movement to critical systems and cloud accounts, the deployment of other malware and ransomware, and data leakage. |